Introduction to Mining Cryptocurrencies: What You Need to Know
Introduction to Mining Cryptocurrencies: What You Need to Know Introduction to Mining Cryptocurrencies: What You Need to Know

Cover art/illustration via CryptoSlate. Image includes combined content which may include AI-generated content.
If you’re new to the crypto space, you may feel a bit overwhelmed. Fortunately, it’s easier to understand than you might think. This guide is for beginners with little to no prior understanding of cryptocurrency or mining. Cryptocurrencies are the future; the time is now to understand how they work and more importantly, how they can help you.
Understanding The Basics

Bitcoin is the first virtual currency that utilizes a completely peer-to-peer network. This is huge. Before Bitcoin, all currency was controlled by either a bank, credit card company, or government.
It is revolutionary because it gives its users control. In fact, Bitcoin wouldn’t be around without its users. It’s a decentralized currency meaning it’s not controlled by one single entity. It allows everyone on the network to share data amongst everyone else.
Well, plenty of people illegally download copies of data like songs and movies from the internet, so what’s stopping people from sending the same Bitcoin twice?
Unlike files that can be downloaded from the internet like an MP3 or a JPEG, a Bitcoin can’t be copied or duplicated. Every time a transaction is made (Bob sends Gary a Bitcoin) it is visible on a public database called the blockchain.
Everyone who owns Bitcoin can see the data on the blockchain. This includes information like a transaction amount and the wallet address. Every single Bitcoin transaction since its creation is stored on the blockchain. However, it doesn’t show the name of the sender, recipient, or any identifiable information. Bitcoin is a safe and encrypted way to pay.
Although the blockchain is one central database, it’s not controlled by one central entity. Bitcoin is decentralized, meaning it’s not controlled or managed by one entity. It’s controlled by the people as mentioned before. If you’re having trouble understanding this concept so far, here’s a great video that might help:
Everyone has their own copy of the blockchain, which is also often referred to as the ledger. Everyone is keeping track of the same thing, comparing what they have amongst each other to ensure everything matches up correctly.
Each time a transaction is made, an announcement is made to the rest of the network. Everyone can see your wallet account number, the number of the account you’re sending Bitcoins to, and the amount of Bitcoins you’re sending.
If everyone has access to the blockchain, how do we know it’s secure?
Cryptography is the method in which a transaction is validated for the blockchain.
This system utilizes bits and pieces of information called keys. It’s a mathematical guarantee that the transaction is legitimate.
In order to verify the network, mathematical equations are solved. Different currencies use different algorithms, Bitcoin’s algorithm being SHA-256. These algorithms are called cryptographic hash functions.
The cryptographic hash function is solved by guessing and checking numbers until the solution is found. On average, it takes about 10 minutes to solve each problem. This is why Bitcoin’s “block time” is 10 minutes. Different currencies use different algorithms and have different block times.

Among a few of the downsides to this system are transaction delays. Since the network is verified by the users, it takes a while for a transaction to occur. Unlike a credit or debit card which both provide instantaneous transactions, Bitcoin transactions take a bit longer.
When you send or receive a Bitcoin, it must be verified about 6 times before the transaction is validated. Since each block takes about 10 minutes, you won’t see Bitcoin appear in your wallet until about an hour after it’s been sent.
Whoever solves the problem first gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain. Keep in mind these computers are guessing and checking billions of combinations before they find the solution.
The people who run their computers day and night to verify the network consume loads of electricity. Of course, they don’t do it for free. Right now, each time a block is solved the person running the hardware is awarded 12.5 Bitcoins. These people are most commonly referred to as miners and the process of verifying the network is referred to as mining.
There are only 21,000,000 million Bitcoins available to be mined. They’re in limited supply, and as the amount left to mine diminishes, the price increases.
When Bitcoin was first developed the block reward for solving a cryptographic hash function was 50 BTC, and a Bitcoin wasn’t worth much at all. The block reward halves after every 210,000 blocks. At this point, we’re down to 12.5 Bitcoins per block reward.
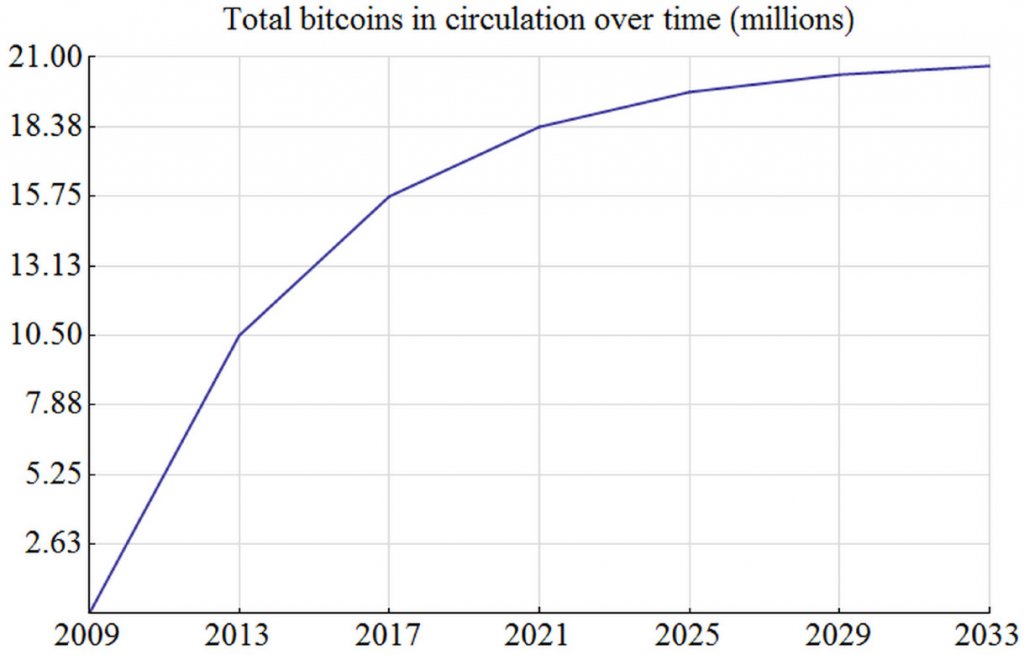
So, what happens after they’re all mined?
When you send or receive a Bitcoin you must pay a small transaction fee. These transaction fees are given to miners almost like giving a tip. When there aren’t any more Bitcoins left to be given to miners, they’ll still receive the transaction fees.
We expect the amount of transactions to be so high at that point in time that the mining incentive will be the same. Even after the entire supply of Bitcoin have been mined, people will still be mining to verify the network. Just like gold, the value of Bitcoin rises as the supply is depleted.
Bitcoin Mining: Is It Profitable?
Now that you know how Bitcoin mining works you may be eager to set up your very first mining rig.
Unfortunately, we have some bad news. Altcoin mining in 2018 is profitable; however, it’s difficult to turn a profit by mining Bitcoin at this time.
You might be wondering why, as the current block reward is over $100,000. All you have to do is buy mining hardware and let loose, right?
Not quite.

It’s extremely difficult to successfully validate the network and receive the block reward. Odds are you won’t see any profits at all with regular mining hardware. You’d be better off joining a Bitcoin mining pool. A mining pool is a group of people who all work on solving the same problem together. Their likelihood of successfully validating the block are much higher this way, and they split the profits evenly based on how much they contributed.
Originally CPUs (processors) were used for mining, but it was quickly discovered that the GPU is far better equipped for solving cryptographic hash functions. Eventually ASICs (Application Specific Integrated Circuits) were developed specifically for mining.
Most Bitcoin mining is done in places with a low cost of electricity. In the United States the average electricity cost is around twelve to thirteen cents per kilowatt hour. In places like China, it may be as low as seven to eight cents per kilowatt hour.
Big companies spend millions of dollars on hundreds if not thousands of ASICs, not to mention the cost of hiring IT people to set everything up. They have them all running at one time, 24/7 in a warehouse in a place with low electricity cost, like China as mentioned above.

This makes it hard for your average Joe who only has enough to buy one miner. Their odds of profitably mining are pretty low.
Another problem caused by the development of ASIC cards is that they make it harder for the currency to be decentralized.

Remember, Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer network. Everyone can see the ledger, and the ledger is validated by all of the miners. It’s shared. Of course, when one person or company is doing a huge percent of the mining, it becomes more centralized.
ASICs are pretty expensive and most people with an average salary can’t afford to spend $2,000-$6,000 on expensive ASIC mining hardware.
Regular (and affordable) GPUs that used to mine Bitcoin aren’t powerful enough anymore and have become obsolete. Only large mining corporations have the funds to support a profitable mining operation.
This is one of the reasons why newer altcoins such as Vertcoin are ASIC resistant. Their mining algorithm becomes progressively harder to stay ahead of the development of an ASIC card.
This way, everyone can afford to mine which keeps the power out of one person or company’s hands.
What Coins Should You Mine?
If you’re looking to generate passive income through mining, we suggest you look elsewhere to get started. Mining coins like Ethereum, Litecoin, Monero, and Dash are far more profitable than mining for Bitcoin.
Here’s an added bonus: you can exchange your mined altcoins for Bitcoin on popular exchanges like Binance and Bittrex.
You can find plenty of pages with great information regarding mining hardware. For example, if you’re looking to mine Ethereum simply search “ethereum mining hardware” and you’ll find the information you’re looking for.
What is the Best Mining Hardware?
It really depends on the coin you’re mining. Different coins have different algorithms meaning different cards will have different hashrates.
You’ll have to check out mining guides for the mining GPUs or ASICs you’re looking at depending on the coin, as hashrates will vary. Serious mining rigs are not housed in traditional PC cases, but rather multiple GPUs are configured in a mining rig.
What’s Hashrate?
To answer this question, we’ll have to think back to the problem. Your mining hardware is solving cryptographic hash functions by guessing and checking solutions until it finds the right answer.
Basically a hashrate is how fast your hardware can guess and check answers.
The higher the hashrate, the faster and more likely you are to solve the problem.
The most important thing to look at is the hashrate/power consumption ratio. If your mining hardware has a low hashrate and a high power consumption then you’ll end up losing money in electricity costs.
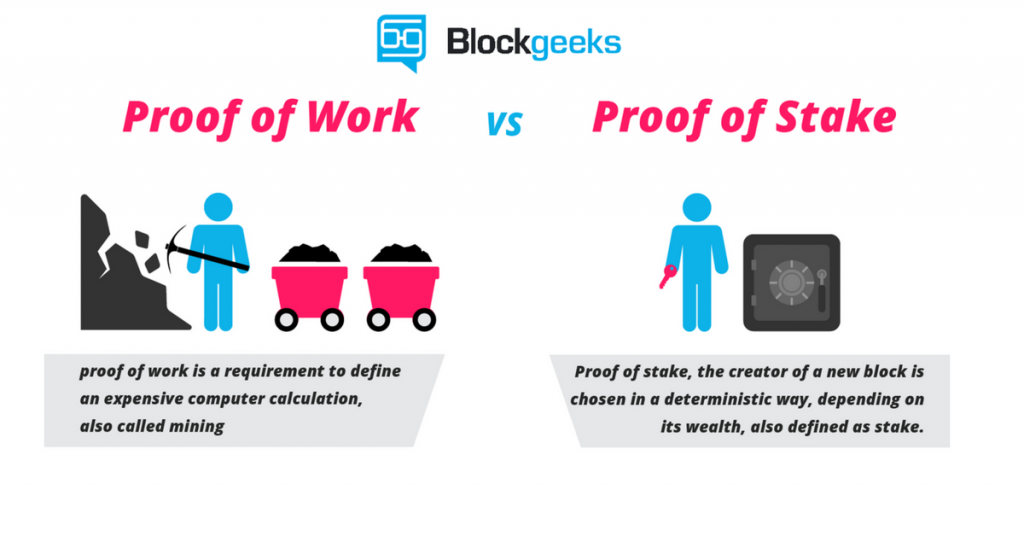
By the way, Bitcoin and many other coins use a Proof-of-Work or PoW system. You’re exchanging electricity and power costs for Bitcoin.
Right now the most powerful Ethereum miner is the Radeon R9 295X2. It’s hashrate is sitting at around 46 MH/s. (That means 4,600 hashes per second.) Its max power consumption is around 500 W from the wall with stock frequencies.
We can plug these two numbers along with a power cost of twelve cents per kilowatt hour into an Ethereum mining profitability calculator and project our estimated earnings.
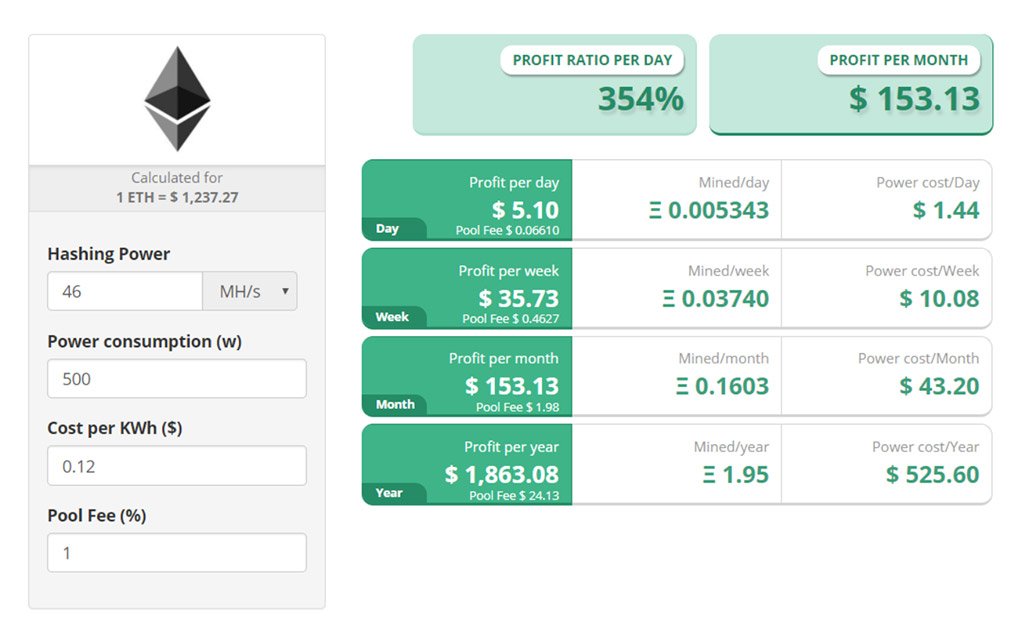
You can expect to rake in nearly $2,000 with this mining hardware. I has the highest hashrate among Ethereum miners and a comparatively low power consumption; although, it doesn’t necessarily mean it’s the best choice.
For example, the GTX 1050 Ti hashrate sits at around 12 MH/s and a power consumption of around 70 W. Right off the bat it’s obvious that the hashrate is only a quarter of the 295X2’s hashrate.
Remember when we mentioned the hashrate/power consumption ratio? Well, it’s really going to come into play here.
The R9 295X2 costs around $600 whereas the GTX 1050 Ti only costs around $150. Let’s say you had the choice of buying one R9 295X2 GPU or four 1050 Ti GPUs as they both cost the same.
The combined hashing power of four GTX 1050 Ti GPUs is about 46 MH/s but the combined power consumption is only 280 W. You’re getting the same hashing power and a lower electricity bill! Take a look:
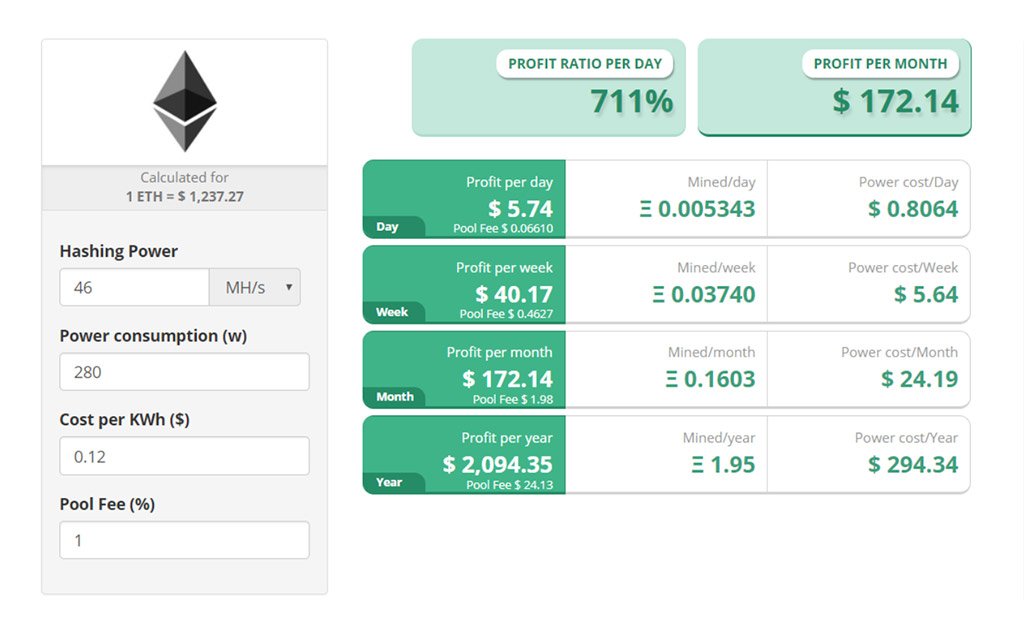 You can mine with almost any GPU, but some are better than others. Most newer GPUs that are gaming oriented are a safe bet. Something about the architecture used for gaming is also great for mining!
You can mine with almost any GPU, but some are better than others. Most newer GPUs that are gaming oriented are a safe bet. Something about the architecture used for gaming is also great for mining!
It’s always a good idea to check your specific GPUs hashrate/power consumption ratio first. For example, even though the GTX 1080 and 1080 Ti are absolute monsters when it comes to gaming, for some reason they’re not the best mining GPUs on the market.
Don’t get me wrong, they’re more than capable. The GTX 1080 hashrate is around 20 MH/s which isn’t bad, but there are better options out there. The RX 580 doesn’t even compare to the GTX 1080 in the gaming realm. However, the RX 580 hashrate is around 25 MH/s.
You’ll also want to make sure your mining GPUs stay cool during operation. Most miners mount their GPUs in a mining rig frame as opposed to a traditional case. GPUs expel a lot of heat, and if you’re pushing your cryptocurrency mining hardware to the max, even the best case fans may struggle to cool down several GPUs running in an SLI/Crossfire configuration.
Moral of the story?
Do your research before you buy. Don’t be fooled into thinking you’ll become a millionaire with any old GPU. If you learn as much as you can and get the proper mining equipment, you can generate substantial passive income!