Introduction to NEM (XEM): The Proof-of-Importance Coin
Introduction to NEM (XEM): The Proof-of-Importance Coin Introduction to NEM (XEM): The Proof-of-Importance Coin

Cover art/illustration via CryptoSlate. Image includes combined content which may include AI-generated content.
Many of the top blockchains, such as Litecoin and Bitcoin Cash are either hard forks or software branches of the original Bitcoin code and blockchain. However, that is not the case with NEM. It’s built with 100% original code. NEM has done away with Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake – instead, NEM is the first cryptocurrency to use the “Proof-of-Importance” algorithm.
The new consensus system provides fast transactions, minuscule fees, low power consumption and 100% transparency – the development team designed NEM to be a functional coin in today’s economy.
Formerly known as the New Economy Movement, NEM (ticker: XEM) aspires to become the new medium for everyday exchanges in addition to the common enterprise use cases that many blockchain projects seek to become. Transactions appear in your wallet in 5 seconds and are confirmed in just 20 seconds. Moreover, the network is known to handle 3,000 transactions per second.
NEM History

NEM was founded by a Bitcointalk user who called himself by the username “UtopianFuture.” Initially he wanted to improve on Nxt, but eventually, he and a group of devs decided they would start from scratch.
The project was launched in March 2015 – a group of 15 developers and nearly 30 marketers comprised the NEM.io team. Founded in Singapore, they are the driving force behind the token and thus far, have chosen to remain pseudonymous.
Proof-of-Importance
The Proof-of-Importance algorithm does not make use of expensive mining hardware, instead, harvesters are in charge of validating the network.
What is a harvester? This is simply someone who is staking their coins to assist in network validation. Anyone can harvest the NEM network. As a result, a substantial amount of energy is conserved. Sending a payment on the Bitcoin network consumes 100x more electricity than the NEM network.
Before you can begin harvesting, you will need at least 10,000 XEM vested in your account. Once XEM is purchased and stored in your Nano Wallet, 10% of your wallet’s balance becomes vested every 24 hours. For example, if you bought 100,000 XEM, 10,000 would be vested after one day and you’d be ready to start harvesting.
Harvesters connect to a supernode, a high-performance node that is required to run 24 hours a day, seven days a week. One must have 3,000,000 XEM vested before they can run a supernode.
The NEM Blog explains:
The NEM network has been designed from the very beginning with the goal in mind that any light client can securely connect to and use any server safely to make any transaction. Supernodes are expected to be high performance and reliable nodes. They are regularly tested on their bandwidth, chain height, chain parts, computing power, version, ping, and responsiveness to make sure that they are performing to high standards.
The POI network looks at three things when determining who gets to verify transactions:
- The amount of XEM is in your wallet
- How long it’s been there
- The quality and number of your transactions
NEM solves one of Proof-of-Stake’s notable flaws: those with the most stake have a higher chance of verifying transactions.
NEM assigns consensus addresses and importance scores to everyone on the network. You can think of the importance score like a rating of trust or reputation. The higher your score, the more trusted you are by the network to verify transactions.

Your chance of successfully verifying the network is not solely dependent on how much you have at stake – rather, it is based on how many transactions you have made in the past, and the quality of those transactions.
Sending 1,000 XEM to another account that has already vested 10,000 XEM is an example of a quality transaction. Setting up a bunch of accounts and sending XEM between them will not be enough. If an account sends XEM and receives the same XEM back again, it will lower the account’s importance score.
You will never need to download anything to harvest, nor will you need powerful hardware. As long as you’re connected to the supernode, your importance score is borrowed. In return, you’re permitted to keep some of the transaction fees from the blocks they process.
Namespaces, Mosaics, and Smart Assets
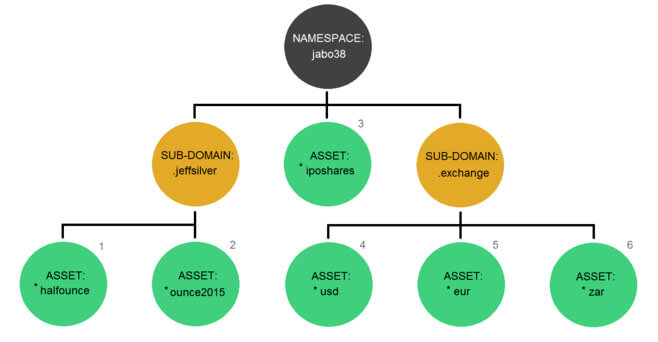
Namespaces are an important part of NEM’s economic ecosystem. You can think of a Namespace like a website domain. Namespaces appear unique in the NEM network. Just like website domains that have sub-domains, Namespaces can have sub-namespaces.
The NEM Blog helpfully explains:
The basic things you need to know about NEM’s recent fork are Namespaces and Mosaics features. The easiest way to appreciate it is the domain and file analogy on the internet. Imagine that a domain address has to be unique in a root (lowest level). Namespace addresses this unique feature. If one creates a Namespace, that Namespace will appear unique in the NEM ecosystem.
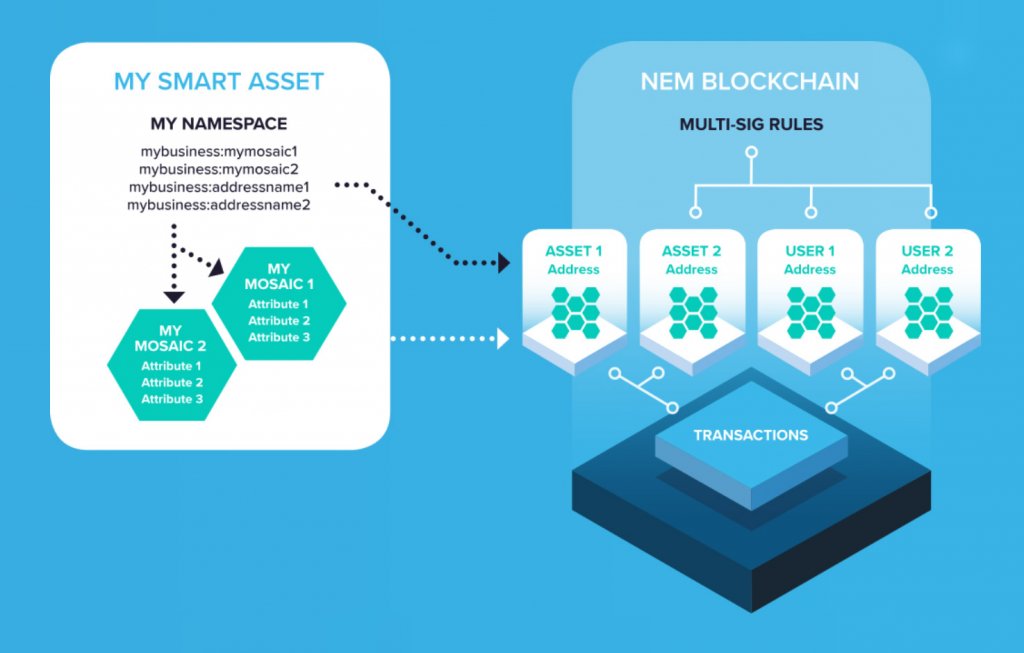
Namespaces open the door for the creation of Mosaics. You can think of a Mosaic-like a file hosted on a domain. Mosaics represent a digital asset, and they are stored under unique Namespaces and sub-namespaces on the NEM blockchain.
In practice, Mosaics are NEM’s built-in tokens. XEM is technically considered a Mosaic on the NEM network. For example, you could create a cryptocurrency called “MilkshakeCoin” and announce that each token is worth one Milkshake from your restaurant. Mosaics are especially advantageous for enterprise use.
You can also use mosaics to store music licenses and contracts – anything you can sell or trade can become a mosaic on the NEM network.
Mosaics are the building blocks of the Smart Asset system.
Similar to Ethereum’s Smart Contracts, NEM’s Smart Asset system allows developers to code NEM applications with ease – the network can be used for more than peer-to-peer exchanges.
Through the use of Namespaces, Mosaics, and Smart Assets, the NEM network can manage legal documents, energy usage, supply chains, real estate titles and cryptocurrencies. For example, the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture is currently using NEM to track shipments of wild game meat on the NEM blockchain.
Other Noteworthy Features
NEM offers two blockchain varieties: the public NEM blockchain and the private blockchain, named Mijin. Over 300 companies are using the private Mijin blockchain. More often than not, each application of the private blockchain is unique.
For example, some companies use it for tracking shipments, while others have used it for currency remittance.
NEM.io explains why Mijin is beneficial for businesses:
Public blockchains such as NEM allow anyone to join the network to freely share and receive data. However, most businesses require their information to be kept confidential. In such cases, NEM provides a customizable approach through their permissioned ledgers an based on NEM technology, Mijin provides this powerful functionality. In such cases, NEM provides a customizable approach through a private permissioned ledger option based on the same NEM platform technology. Tech Bureau provides an excellent packaged NEM private blockchain solution in the form of their Mijin product.
A “crypto FinTech laboratory” called Tech Bureau is the company developing this new blockchain technology based on NEM. The latest installment of the Mijin network, Catapult, was designed by Tech Bureau in conjunction with the NEM core developers.
NEM.io’s blog has this to say regarding the release of Catapult:
The project codenamed, ‘Catapult’, is a newly amended and augmented version of the current Mijin platform that Tech Bureau has developed previously with the NEM core developers. With this architecture, Mijin and NEM shall be creating yet another first in the crypto-sphere. Catapult will mark the beginning of an enterprise-class approach. It will create a new standard of design and is unprecedented in the blockchain domain, lifting its bar.
With Catapult, NEM’s engine was rebuilt to maximize blockchain performance. It is capable of making international transactions in mere seconds. Catapult is also secure enough to become the long-term platform for a banking services company. Later this year, Catapult is expected to launch on the public NEM blockchain.
This token was designed for functionality, and can easily be adopted by businesses – over 300 are already using NEM.
NEM is 100% traceable. This trait is essential for widespread business adoption of the coin. Unlike privacy coins such as Monero, all transactions made on the NEM network are entirely public. Some privacy advocates may dislike this feature, but it is a must for use in the world of business, where a public record of transactions is essential.
Businesses have to keep a record of transactions, not only for financial purposes but also to track spending habits for targetted advertising. If they were completely encrypted, NEM would have a difficult time being adopted for its intended use.
They also offer multi-signature accounts, useful for families and businesses. For example, if a college student wants to withdraw from their college fund, they would need a parent’s signature beforehand.
A Better Way to Pay?
NEM’s low transaction fee is among its most compelling characteristics. It is even cheaper than mainstream e-commerce payment solutions, such as PayPal, Apple Pay, Venmo, etc.
The network takes a 0.01% fee of all transactions as a reward for harvesting. Only $0.01 is required to send $100, or $0.10 cents to send $1,000. Contrary to Bitcoin’s high transaction fees, NEM’s are next to nothing.
Inflation Resistant
When NEM was created back in 2015, 8,999,999,999 XEM were distributed among 1,500 trusted individuals. Inflation is impossible because there will never be any more XEM minted.
When a block is successfully harvested, new XEM is not created as a reward. Instead, transaction fees from harvested blocks are collected. Some blocks may be full of transactions, while others contain scarcely any. Block rewards are random, although running a supernode is more profitable than merely harvesting the network.
NEM Voting Module
NEM has a voting module built into their Nano Wallet GUI. It allows anyone to vote as long as they have 10,000 XEM vested in their account.
Unlike Decred, voters are not rewarded for their vote. Nevertheless, NEM has its unique way of voting. Remember the importance score mentioned previously? It comes into play once again with NEM’s voting system. A vote from an account with a high importance score carries more weight than a vote from an account with a low importance score.
Meet NEM.io’s President
Lon Wong is the President of the NEM.io Foundation. He is also the founder and CEO of Dragonfly Fintech Pte Ltd, a blockchain technology company.
Wong has been an entrepreneur for more than 30 years, and he has experience with electrical engineering, controls and automation, network and infrastructure design, and software design.
Wong attended The University of New South Wales in Australia, receiving a Bachelor’s degree in Electrical Engineering. On Wong’s LinkedIn profile, he remarks:
Currently, I take particular interest in the NEM blockchain technology. As President of the international open source NEM.io Foundation, and a core team member of this cutting edge open source blockchain technology, I have been instrumental in contributing to the best of breed design of the NEM blockchain solution that will find its place in the financial industry. I believe we are in a strong position to embark on yet another project based on the blockchain technology.
It will be interesting to see what Wong has to offer for the NEM.io Foundation in 2018.
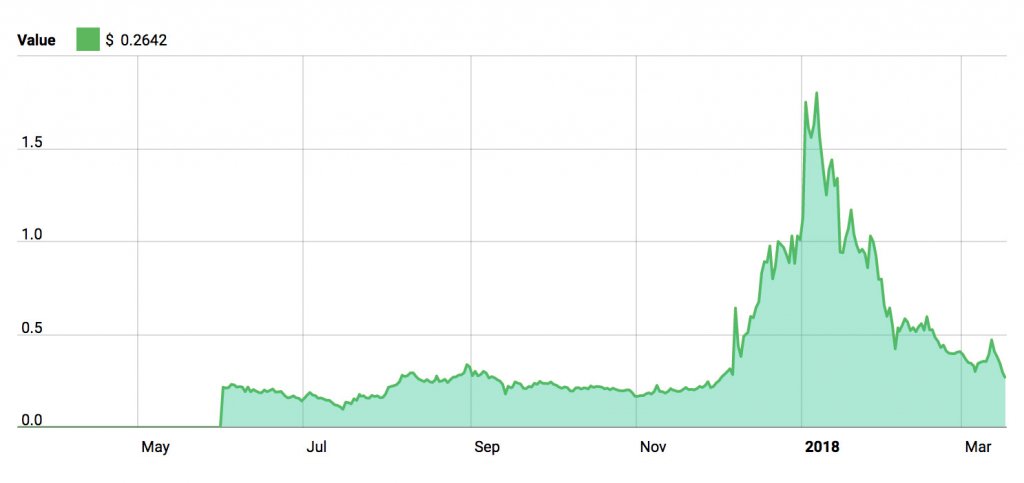
Recent Price Movement
On January 6th, 2018, NEM hit a high of $1.80. Over the past two months, the entire cryptocurrency market has fallen into a slump, so it is currently trading at $0.38.
Where to Buy
NEM is currently trading on Bittrex, Poloniex, Zaif, UpBit, Huobi, and Zaif. NEM can also be purchased directly through the Nano Wallet GUI.
Community
NEM has a substantial community on their official forum – you can browse over 1,000 threads and a tech support section.
There is a strong community of project supporters (16,000+) in the NEM subreddit, in addition to an impressively large thread on Bitcointalk with more than 1,800 pages of information.
Conclusion
Contrasting Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work algorithm, NEM saves electricity and facilitates fast payments with minuscule fees. Improving upon Proof-of-Stake, NEM doesn’t solely reward its users based on the quantity of XEM in their wallet, but their network participation as well.
NEM is currently among the most popular cryptocurrencies in Japan, and it is among the top ten largest cryptocurrencies by market cap according to CryptoSlate’s coin rankings.
However, harvesting is not as profitable compared to mining other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum. Fortunately, based on NEM’s algorithm, block rewards should become more significant as network participation increases. It will be compelling to see what happens next with this economic ecosystem.
For more information about NEM, including current price, market cap, technical information and social media links, please check out our NEM coin profile.




 CoinGlass
CoinGlass 


 Farside Investors
Farside Investors