Steady influx of stablecoins helps fuel Bitcoin price surge
Steady influx of stablecoins helps fuel Bitcoin price surge Steady influx of stablecoins helps fuel Bitcoin price surge
Stablecoins flex their buying power, catalyzing Bitcoin's price surge
Quick Take
Recent data analysis reveals a steady influx of stablecoins into Bitcoin, a phenomenon underpinned by the Stablecoin Supply Ratio (SSR) created by Glassnode. The SSR denotes the ratio between Bitcoin’s supply and that of stablecoins, with the calculation formula being: Bitcoin Market cap divided by Stablecoin Market cap.
Notably, the stablecoins considered in this framework include USDT, TUSD, USDC, USDP, GUSD, DAI, SAI, and BUSD. A lower SSR implies that the current stablecoin supply wields a greater “buying power” to purchase Bitcoin. The ratio, however, has exhibited an upward trajectory over the past few weeks, indicating an increase in Bitcoin purchases using stablecoins.
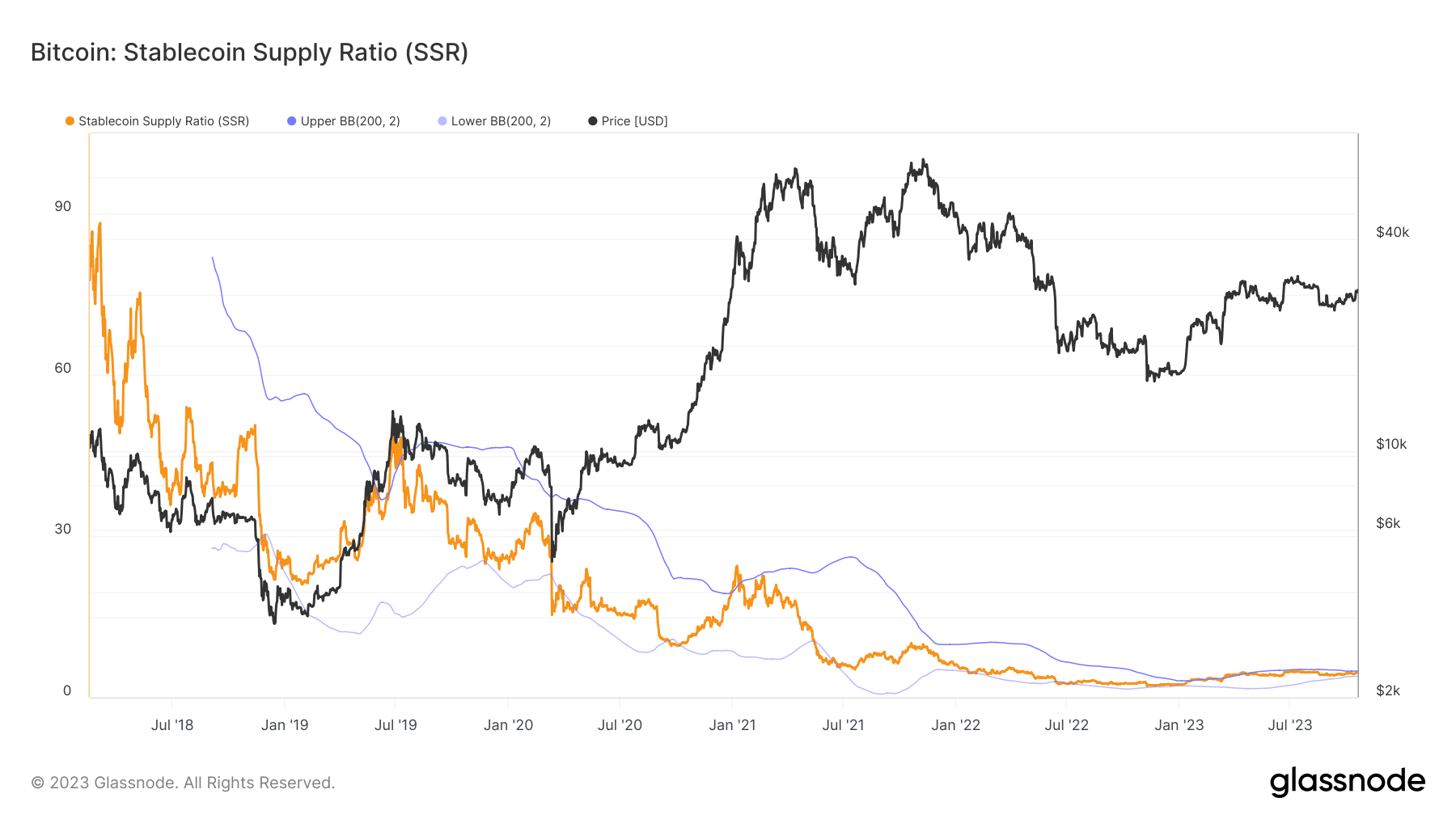
Additionally, the analysis showcases the relevance of the Stablecoin Oscillator, an SSR derivative, that quantifies the SSR’s 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) movement inside Bollinger Bands BB(200, 2).
On Oct. 14, the Oscillator crossed the threshold of 0 and has been rising since then, reaching 0.99. This upward trajectory is believed to be one of many catalysts in the surge of Bitcoin’s price. The increase in the SSR oscillator, as indicated by the red arrows below, appears to have facilitated previous rallies in Bitcoin.
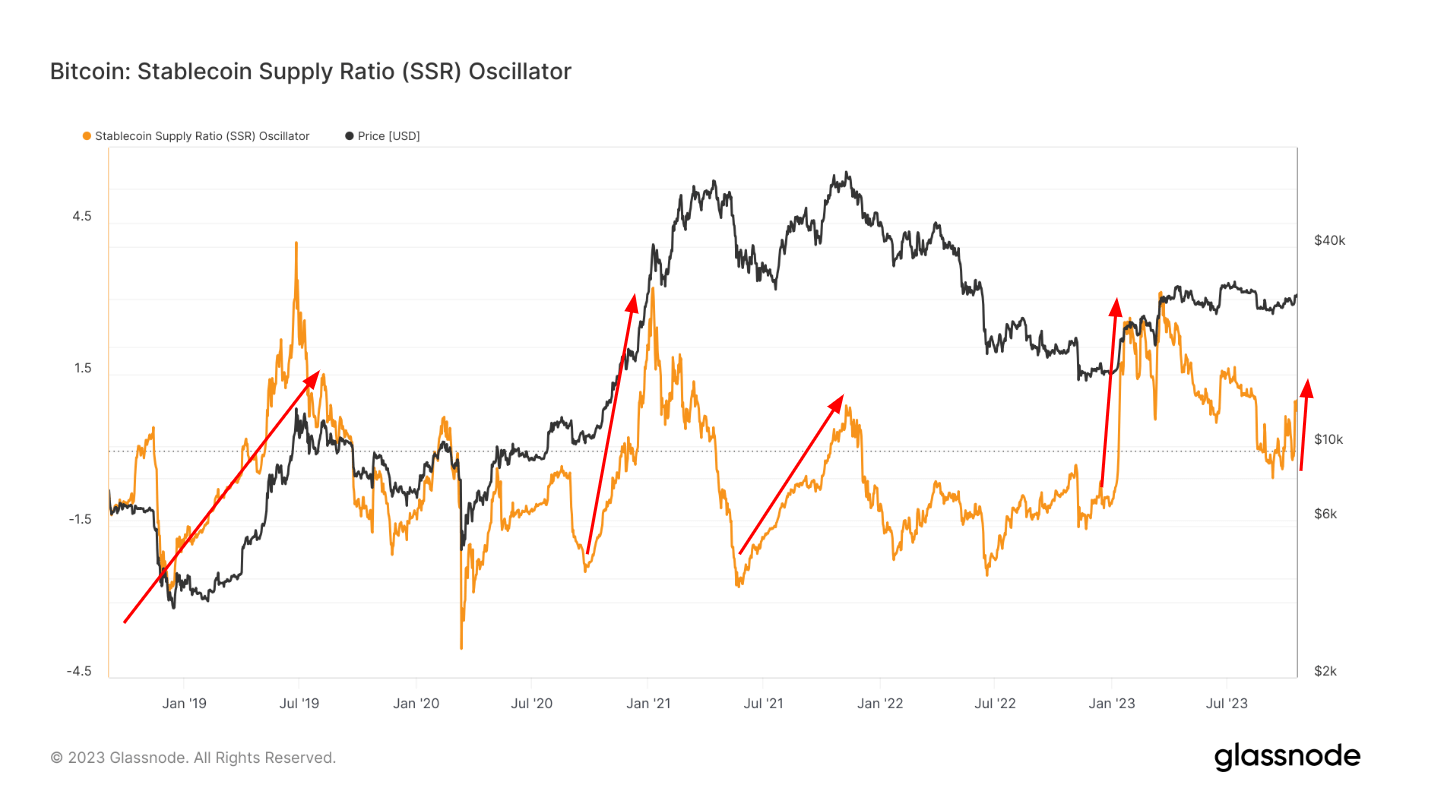
Additionally, the outflow of stablecoins on exchanges appears to have halted, maintaining a steady level since June at approximately $18.5 billion. This represents a substantial reduction of about $25 billion from its peak to its lowest point in the same timeframe last year.




 Arkham Intelligence
Arkham Intelligence 

 Farside Investors
Farside Investors 
 CryptoQuant
CryptoQuant 
 CoinGlass
CoinGlass