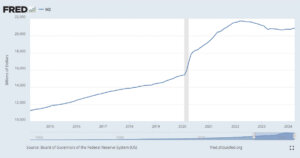
M2 Money Supply
Source: FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (US), M2 [M2SL], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/M2SL, November 16, 2024.
What is M2 Money Supply?
The M2 money supply is a broad measure of the total money supply within an economy. It includes:
M1 Money Supply
- Physical currency and coins in circulation.
- Demand deposits (checking accounts).
- Other liquid deposits.
Near-Money
- Savings accounts.
- Money market mutual funds.
- Other time deposits that are less liquid than M1 but still easily convertible to cash.
History of M2 Money Supply
The concept of categorizing money supplies into different measures like M1 and M2 originated in the mid-20th century as central banks and economists sought to better understand and control the monetary system.
- 1950s-1970s: Central banks, including the Federal Reserve, began publishing data on different money supply measures. M2 was created to offer a broader perspective than M1, which only included the most liquid forms of money.
- 1980s-2000s: The relevance of M2 grew as the global economy expanded and financial markets became more complex. Central banks used M2 to gauge the overall liquidity in the economy and its potential inflationary effects.
- 2008 Financial Crisis: The importance of M2 surged during the crisis, as central banks massively increased the money supply to stabilize financial systems. Quantitative easing (QE) programs led to significant growth in M2.
- 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic: The response to the pandemic saw unprecedented increases in M2 as governments and central banks injected trillions into the economy to support businesses and individuals.
M2 Money Supply and Bitcoin
Correlation and Relationship
Bitcoin, as a decentralized digital asset, has often been analyzed in the context of traditional financial metrics, including M2.
- Hedge Against Inflation:
- As central banks increased the M2 supply, especially during crises, fears of inflation grew. Bitcoin emerged as a potential hedge against this inflation, similar to gold.
- When M2 grows rapidly, investors often seek assets that can preserve value, leading to increased interest in Bitcoin.
- Store of Value:
- Bitcoin’s fixed supply of 21 million coins contrasts with the flexible supply of fiat currencies. The expansion of M2 can devalue fiat currencies, making Bitcoin attractive as a store of value.
- Historical data shows periods of rapid M2 expansion often coincide with significant Bitcoin price increases, suggesting a correlation between the perception of fiat devaluation and Bitcoin’s appeal.
- Liquidity and Investment:
- Increased M2 can boost liquidity in financial markets. Higher liquidity often leads to more investment in a variety of assets, including Bitcoin.
- During times of high M2 growth, the influx of capital into markets can spill over into the crypto market, driving up Bitcoin prices.
- Economic Uncertainty:
- In times of economic uncertainty, as reflected by aggressive increases in M2, investors may turn to alternative assets. Bitcoin, with its decentralized nature, becomes more attractive as a hedge against systemic risks.
Empirical Data and Trends
- Post-2008 Crisis: Following the 2008 crisis, the M2 supply saw significant growth due to QE programs. Bitcoin, introduced in 2009, saw its value rise exponentially as it gained traction as an alternative asset.
- 2017 Bull Run: The 2017 Bitcoin bull run occurred alongside significant growth in global M2 supplies, reinforcing the perception of Bitcoin as a hedge against fiat devaluation.
- 2020 Pandemic Response: The massive increase in M2 during the pandemic correlated with a dramatic rise in Bitcoin prices, hitting all-time highs by the end of 2020 and into 2021.
The M2 money supply serves as a critical indicator of an economy’s overall liquidity and potential inflation. Its relationship with Bitcoin emphasizes the trends between traditional fiat systems and decentralized digital assets.
As M2 expands, particularly in times of economic crisis, Bitcoin often benefits from its properties as a hedge against inflation and a store of value, drawing increased interest and investment from individuals seeking to protect their wealth. The historical correlation between M2 growth and Bitcoin price increases highlights the interconnectedness of these financial phenomena.




 Farside Investors
Farside Investors 
 CryptoQuant
CryptoQuant