 Will the new monetary order have gold or Bitcoin as its foundation?
Will the new monetary order have gold or Bitcoin as its foundation? Will the new monetary order have gold or Bitcoin as its foundation?

Cover art/illustration via CryptoSlate. Image includes combined content which may include AI-generated content.
The International Monetary Fund describes money as something that serves as a store of value, unit of account, and medium of exchange. Over the years, many things have been used as money including shells, peppercorns, gold and silver.
In ancient times, the value of money was linked to its alternative uses. Peppercorns, for instance, had an intrinsic value given by its uses as a condiment. Using this commodity as money was inconvenient because it was difficult to divide and standardize each unit. As time went by, precious metals became the most attractive choice to serve as money because of their durability, limited supply, replacement cost, and portability.
Gold and silver are a more recent commodity people began using as money, but the inefficiency to move it around gave rise to banks that are responsible for holding the precious metals and providing notes that claimed ownership of those holdings. Every note was backed by real gold and silver deposits. Eventually, the notes were delinked from the precious metals and ‘fiat’ money was born.
A new gold standard
In a recent interview, Peter Schiff, the head of SchiffGold and CEO of Euro Pacific Capital, and Saifedean Ammous, the author of the Bitcoin Standard, discussed the value of fiat currency and the characteristics that make gold and Bitcoin better forms of money.
Peter Schiff argued that when it comes to fiat currencies, what they have in common is that they are fiat—”money by decree.” He believes that fiat money does not have intrinsic value because it is no longer backed by gold, as it was originally, and could result in the collapse of the monetary system.
“In a fiat based system, it is all a question of relativity as far as what is one fiat worth in relation to another one. [As a result, all fiat currencies] are going to sink at different speeds and I think the US dollar is going to sink faster than a number of other currencies that don’t have the same macroeconomic problems that we have.”
Schiff attributed most of the international macroeconomic imbalances to President Richard Nixon’s decision to take the U.S. off the gold standard in 1971. When the U.S. dollar became delinked from gold, primary economies were forced off the gold standard as well because the U.S. dollar represented the main reserve asset around the world. Now, the predicted monetary crisis and the international bubbles could lead to a major financial catastrophe that could result in the global monetary system once again linking paper money with gold.
The U.S. national debt is also a reason for concern. The figure has experienced a sharp increase since 1971 going from $0.5 trillion to $22 trillion.
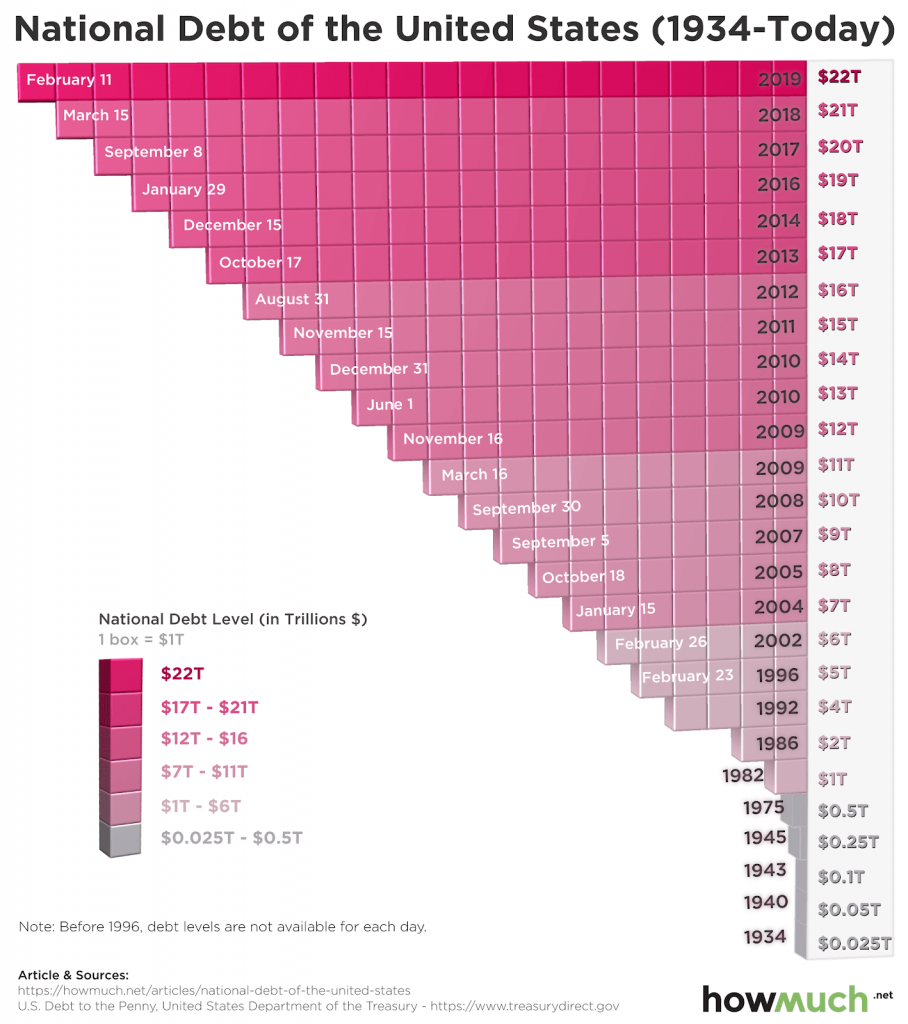
- Source: howmuch.net
A study by the World Bank found that if the debt-to-GDP ratio of a country exceeds 77 percent for an extended period of time then slower economic growth follows. The current debt-to-GDP ratio in the U.S. is at 108 percent, which increases its risk of default since governments around the world may start to doubt a nation’s ability to repay its debt.
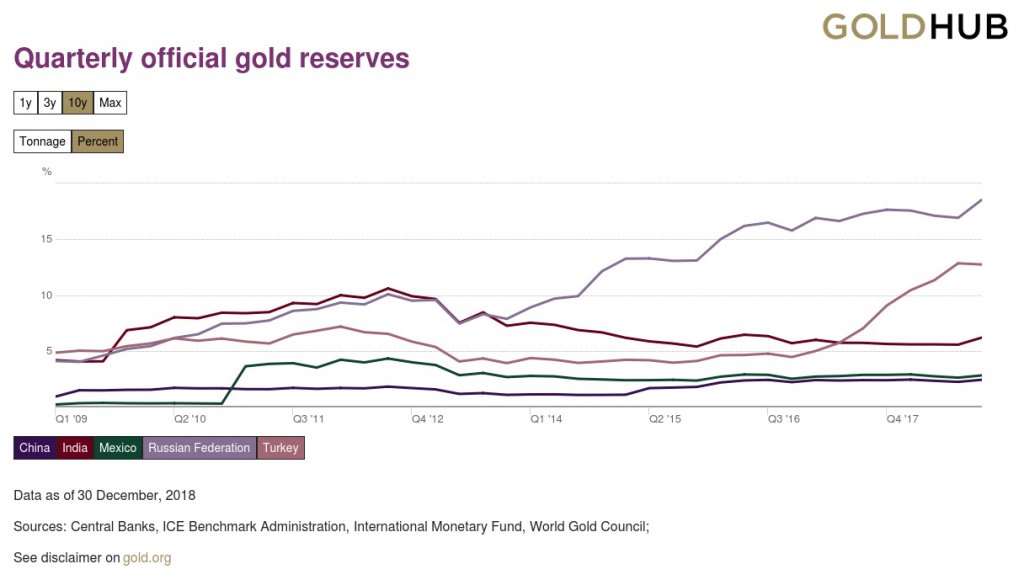
The loss in confidence in the U.S. dollar can also be observed through its use in national reserves. The global economies have been moving away from American money and countries are instead bilaterally trading currencies and commodities outside of USD. As U.S. dollar reserves continue to decline the global gold reserves increase.
“At some point the U.S. dollar will be abandoned as the reserve asset, [and when that happens] foreign central banks are [not] going to look to the euro or the yen or the yuan to replace the dollar. I think they will simply stack up their reserves with gold.”
Under a gold standard, governments will not be able to generate money out of “thin air” since they will have to raise taxes to collect more gold. This will stabilize the money supply, which would grow more slowly over time as governments exercise more control over their expenditures. People will then be encouraged to save and investments will flourish, asserted Schiff.
“If you look at how the US government operated under a gold standard you can see that the consumer price index in the 1800s was at 100 and in the 1900s it was at 50. Under a 100 years of a gold standard prices of other goods relative to gold gradually declined. They lost 50 percent of their value under 100 years so you have a rather slow and steady appreciation of value of money.”

Source: World Gold Council
Bitcoin, the government-resistant currency
Saifedean Ammous agreed that the fact the U.S. dollar is a global reserve currency could mean that the “shelve game” could continue for a while and central banks will find it hard to move away from this currency towards other national currencies. Moving to gold could be the most likely scenario as some central banks are already stockpiling gold, signaling a major shift from the U.S. dollar.
Nonetheless, Ammous sees Bitcoin as the free market alternative to central banks and their monetary measure instead of gold.
“Until 2008, if you wanted to send money anywhere across the world, your only options was to go through central banks. Since bitcoin was invented, we now have a functioning alternative [that could] grow independently off central banks and the banking system that is regulated by governments. It’s going to be a completely free market monetary system built to replace the government of central banks with open source code.”
Saifedean explained that because of the physical nature of gold, moving it around requires significant costs and insurance. Sending gold long distances requires centralized institutions able to organize shipments.
For this to work, it will be necessary to have one gold-receptive bank in every country. This becomes problematic when a local government faces economic turmoil and decides to nationalize its banks, like what is currently happening in Venezuela.
The difference with Bitcoin is that a central bank is not needed. The costs of setting up a Bitcoin node is undoubtedly cheaper than setting up a central bank.
“Bitcoin at its most centralized layer ends up with several thousands nodes and has a most better chance of resisting government intervention,” said Ammous.
Friedrich Hayek, a German economist and philosopher, is often quoted in support of a governmentless currency:
“I don’t believe we shall ever have a good money again before we take the thing out of the hands of government, that is, we can’t take it violently out of the hands of government, all we can do is by some sly roundabout way introduce something they can’t stop.”
Saifedean Ammous conveyed that Bitcoin is indeed “unstoppable” and does not need government and regulation to operate. Even if governments try to shut down the internet to contain the adoption of cryptocurrency, a device that can send 1 or 2 megabytes of data could be used to transact in BTC, making it resistant to any sort of intervention. Many pundits argue mass adoption is inevitable, just as the internet became international just 40 years after its inception.
“The internet [has acted] as a universal protocol for the transfer of data [while] bitcoin [will act] as a universal protocol for the transfer of value. Bitcoin is like the internet. Bitcoin is an open source protocol for exchanging value giving us the basic infrastructure level for movements of value.”
Although Bitcoin is still in the early stages of integrating into the financial system, over the last 10 years, as market and liquidity depth continue to rise as more people believe that it can function as money. Further cementing the one main property Bitcoin needs to succeed—trust.
Carl Menger, an Austrian economist and the founder of the Austrian School of economics, explained in his magnum opus the“Subjective Theory of Value” that the value of a good is largely determined by the importance that people place on that good. The paper emphasizes that “value” is often subjective, and things such as money, which are viewed as intrinsically valuable, stem from people’s perceptions.
As Saifedean Ammous pointed out, Bitcoin may only be 0.1 percent of the total value of money globally. If it is going to succeed as a global currency then it will need to be at least 10-20 percent of the total circulating value of money. As BTC becomes widely accepted, it could become integrated into the global financial system, argues Ammous.
The market will decide
Under the financial crisis that governments across the world are facing, a collapse of the monetary system is possible. Many countries have been taking critical actions to prepare for the worst.
The Russian government, for instance, has been increasing its gold reserves, reaching an all-time high of 2,119 tonnes in the first quarter of this year, in tandem with dumping $101 billion of its U.S. dollar reserves. The Central Bank of Russia also announced that it will create a gold-backed cryptocurrency to facilitate international settlements.
The prime minister of Malaysia, Mahathir Mohamad, made a similar proposal of a new currency based on gold that would be more stable than the Malaysian ringgit, helping economic activity in the region.
While the governments move to gold as a “safe haven” against economic uncertainty, millennials are actually losing interest in traditional hedge assets like gold and are instead opting to hold Bitcoin in their portfolios, according to Nate Geraci, the president of the EFT Store.
In a Bloomberg TV interview, Mr. Geraci disclosed that:
“When we talk to our younger clients–we have a core gold allocation in our portfolios, and they’ll ask about that and say, ‘What about crypto?’ And if you talk to, primarily millennials, and ask them which they prefer, bitcoin or gold, it’s a landslide. It’s not even close, it’s like 90 percent prefer bitcoin.”
Similarly, a Harris Poll revealed that Americans who are 18 to 34-years-old are “very” or “somewhat” likely to purchase Bitcoin within the next five years.
1/ I just published ‘Bitcoin is a Demographic Mega-Trend: Data Analysis’
Which features results from a survey of American adults regarding Bitcoin awareness, familiarity, perception, conviction, propensity to purchase, and actual ownershiphttps://t.co/UlQxfA2zpT
— Spencer Bogart (@CremeDeLaCrypto) April 30, 2019
George Milling-Stanley, the head of gold strategy at State Street Global Advisors, slammed the idea that millennials are using cryptocurrencies as a safe haven because they have lost 80 percent of their value in 2018. However, it seems like millennials are not the only ones seeing the potential that Bitcoin has as a hedge. A recent report by RT showed that Chinese investors have been unloading yuan and moving into BTC and other cryptocurrencies in anticipation of inflation due to the escalating trade war between China and the United States.
Although it is not possible to determine the direction the market will take in respects to a new monetary order, it seems like the powers of the world are stocking up on gold while the newer generations are leaning towards Bitcoin. Politicians have become aware of the financial threats that cryptocurrencies pose to governments due to the lack of control that can be exercised on them, resulting in countries like China eliminating the use, mining, distribution, and exchange of digital assets.
The thread is clear, but the outcome is still unknown. Will a decentralized cryptocurrency become the basis for the global financial system or will the world fall back to gold?


 CoinGlass
CoinGlass  Arkham Intelligence
Arkham Intelligence 

























































































 BTC
BTC