Ethereum merge might have resulted in 40% loss for Hive Blockchain revenue
Ethereum merge might have resulted in 40% loss for Hive Blockchain revenue Ethereum merge might have resulted in 40% loss for Hive Blockchain revenue
The firm has started mining Ethereum Classic and repurposed its Ethereum mining facilities for Bitcoin mining.

Cover art/illustration via CryptoSlate. Image includes combined content which may include AI-generated content.
Bitcoin (BTC) mining analyst Jaran Mellerud estimated that the Ethereum (ETH) merge might have led to a 40% drop in Hive Blockchain’s revenue.
Hive just lost its ether mining cash cow.
I estimate its revenues to have fallen by 40% due to "the merge". pic.twitter.com/1vq0U6EUze
— Jaran Mellerud (@JMellerud) December 5, 2022
Mellerud highlighted that the mining firm’s ETH business was more profitable than its Bitcoin activities, meaning the merge event could lead to a 60% loss in its operating cash flow.
Hive pivots to ETC and Bitcoin mining
The firm has started mining Ethereum Classic (ETC) to remedy the loss. But its main focus is to repurpose its Ethereum mining facilities for BTC mining and increase capacity from 2.8 EH/s to 3.3 by February 2023.
With the miner now looking to go into sustainable Bitcoin mining, Hashrate Index examined its finances to see if it can make this move.
Hive finances remain strong
According to Hashrate Index, the company’s balance sheet looks relatively stable, with only $26 million in interest-bearing debts. This means the company does not have to spend so much on debt servicing and can preserve cash flows, which will help its liquidity.
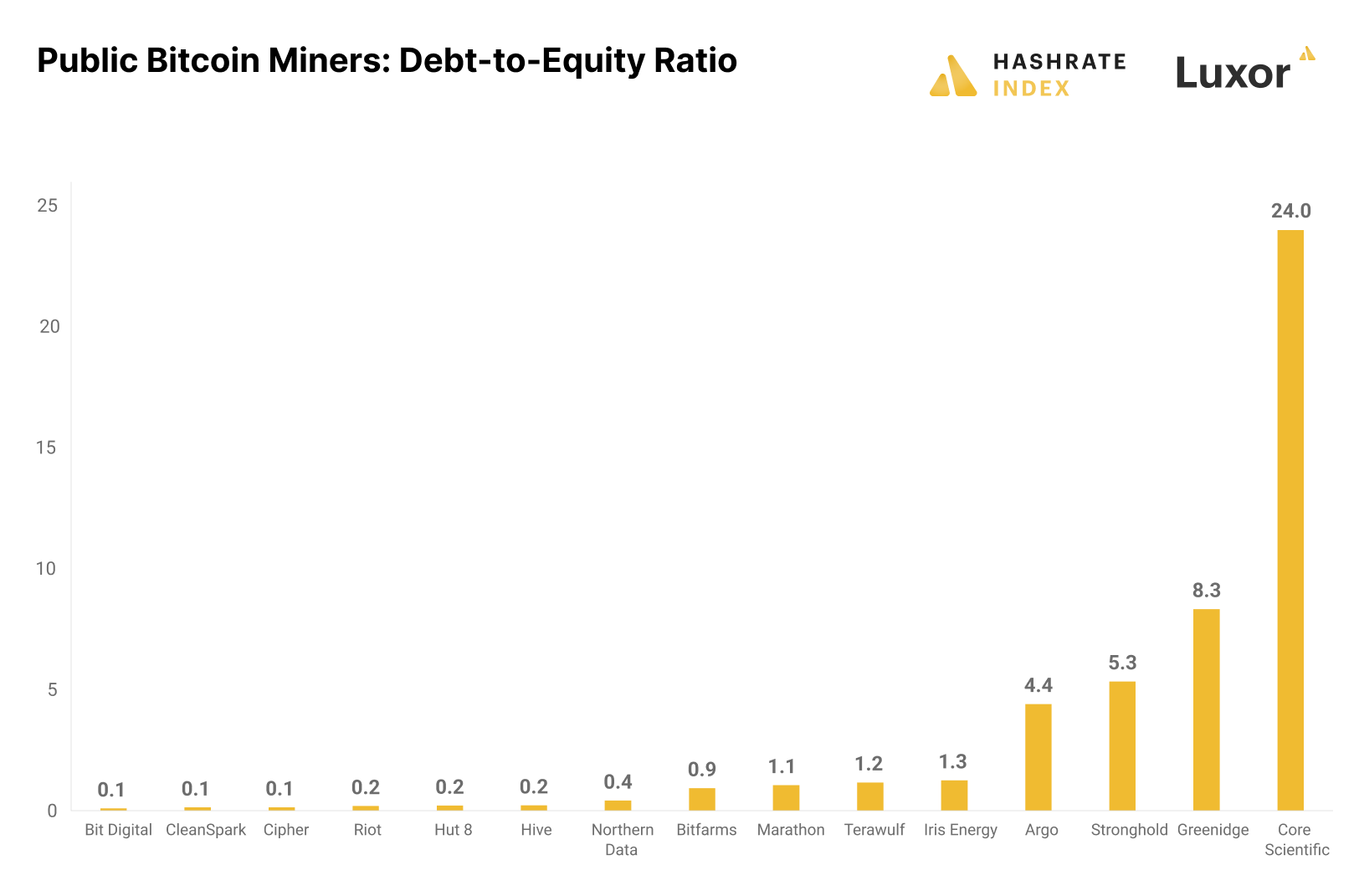
In overall liquidity, the firm has one of the lowest debt-to-equity ratios among public miners and has a quick ratio of 3 for its balance sheet liquidity. Only four other public miners in the top 15 by enterprise value have a more liquid balance sheet.
Its liquidity is mostly in its 3,311 Bitcoin holdings, with only $8 million in cash. At the current value, Hive’s BTC holding is worth $57 million and represents 88% of its liquidity.
The company also has relatively strong gross margins due to its mining operations’ reliance on geothermal and hydro-powered grids. These grids are not exposed to rising energy costs and have lesser downtime.
Hashrate Index wrote that the firm has been able to mine more efficiently, producing between 5% and 30% more BTC than competitors, primarily because of its consistent hydropower supply.
Additionally, the miner has been able to keep administrative costs low compared to competitors like Marathon.
Meanwhile, the massive decline in the value of Bitcoin, coupled with high energy costs and increased mining difficulty, has made BTC mining unprofitable for most miners facing higher operating costs due to debt servicing.