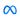Bitcoin fee shifts in transaction trends and market dynamics
Bitcoin fee shifts in transaction trends and market dynamics Onchain Highlights
DEFINITION: The Exchange Fee Dominance metric is defined as the percent amount of total fees paid in transactions related to on-chain exchange activity.
- Deposits: Transactions that include an exchange address as the receiver of funds.
- Withdrawals: Transactions that include an exchange address as the sender of funds.
- In-House: Transactions that include addresses of a single exchange as both the sender and receiver of funds.
- Inter-Exchange: Transactions that include addresses of (distinct) exchanges as both the sender and receiver of funds.
Bitcoin’s exchange fee dominance, represented as a 7-day moving average, has shown significant fluctuations since the beginning of 2024. Notably, the dominance of fees associated with deposits, withdrawals, in-house transfers, and inter-exchange transactions has experienced periods of sharp increase and decline.
In early 2024, a pronounced surge in exchange-related fees occurred, peaking around early February. This spike was primarily driven by heightened activity in deposits and in-house transactions. As the year progressed, exchange fee dominance displayed a cyclical pattern with notable peaks in mid-May and mid-June, coinciding with increased market activity and potential strategic repositioning by investors.
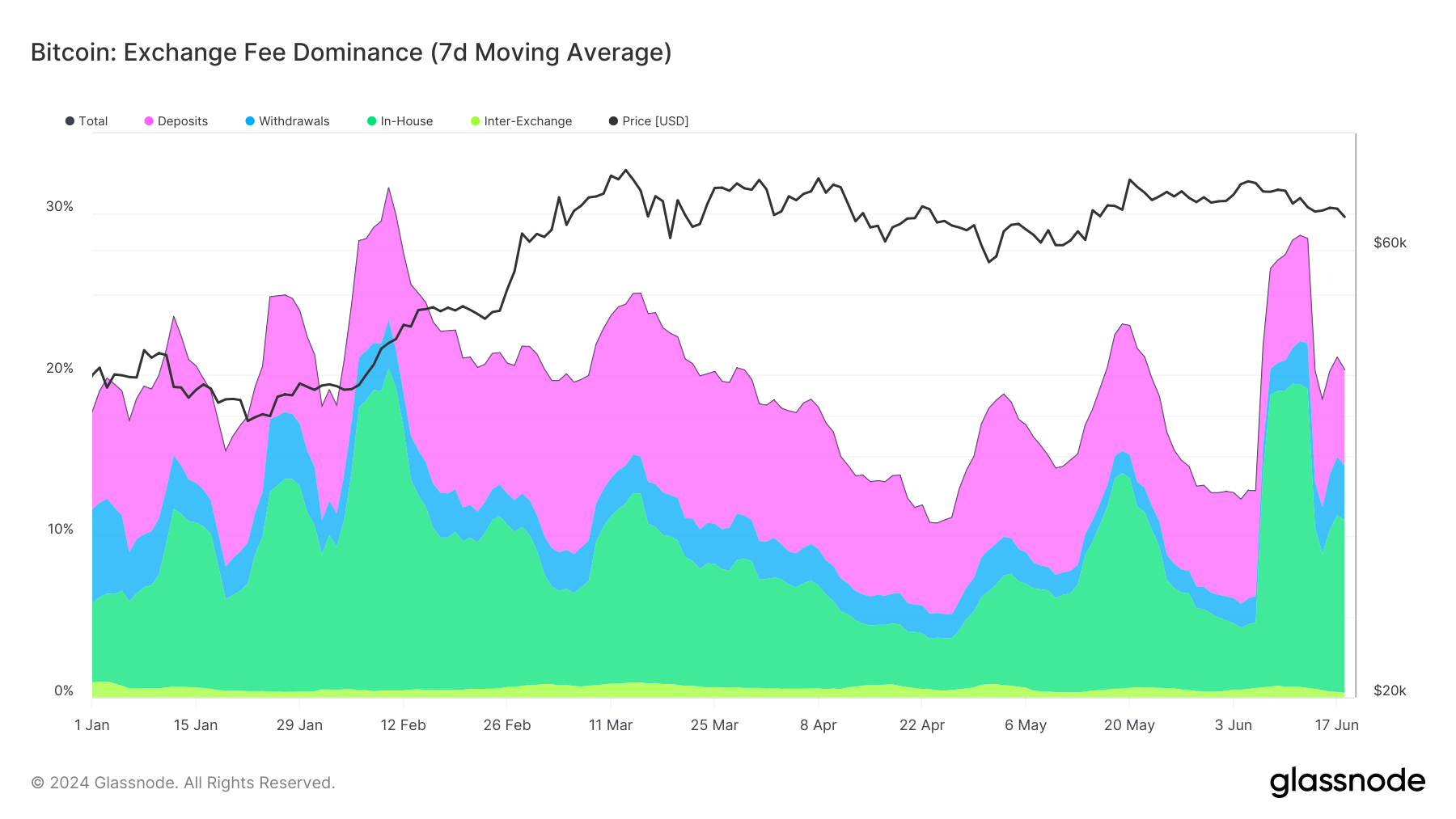
Comparatively, long-term data since 2017 reveal a broader trend of exchange fee dominance aligning closely with major market movements. Significant spikes in exchange-related fees corresponded with critical price milestones, such as the bull runs of late 2017 and early 2021. These periods were marked by substantial market volatility, reflecting increased trading volume and higher on-chain exchange activity.
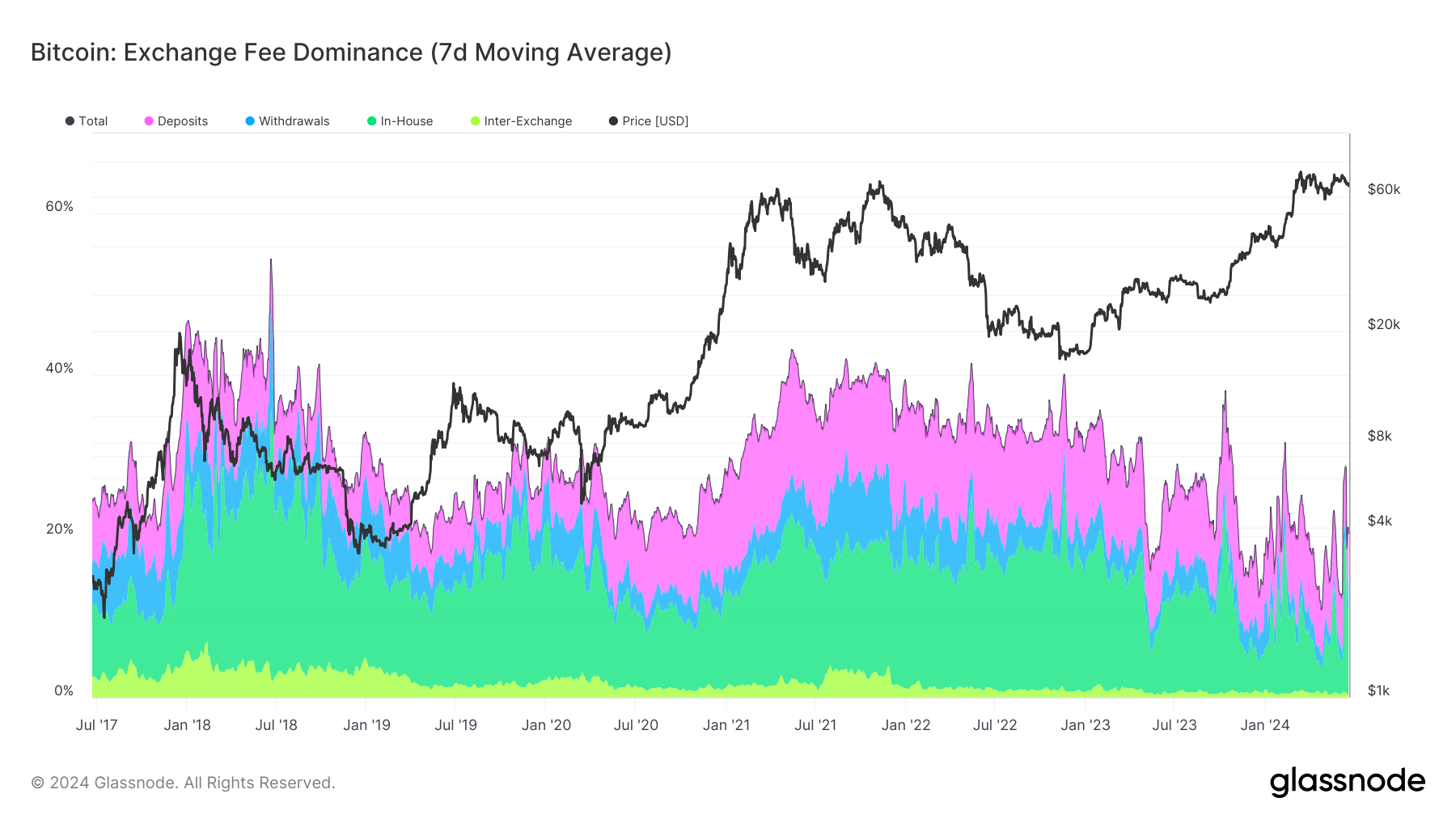
Recent data suggest that Bitcoin’s post-halving price and exchange fee dominance mostly correlate, reflecting broader market conditions and investor behavior. This ongoing interplay emphasizes the significance of exchange-related activities in the Bitcoin ecosystem, influencing transaction costs and overall market liquidity.